Heavy Metal and Mineral Test
20+ Toxic Elements + 20+ Essential Elements
Functional Medicine Test |Heavy Metal Test in Hong Kong - Book an appointment with us to find out heavy metal status in your body, test procedures, and cost.
Functional Medicine Hong Kong Test Service
Excessive Exposure to Heavy Metal
Mineral Imbalance
Minerals such as Calcium, Iron, Potassium and Zinc are vital nutrients that help our bodies function properly. Our bodies cannot produce these minerals on their own. When we don’t get enough minerals from our diet or lack certain nutrients, it can affect how our bodies absorb certain minerals. Not getting the right amount of minerals can result in mineral deficiencies, which can interfere with important bodily functions.
Heavy metal intoxication symptoms
Usual symptoms: diarrhea, nausea, abdominal pain, vomiting, shortness of breath, tingling in your hands and feet, chills, weakness.
There are Metal-specific symptoms as well. For example, mercury poisoning can cause trouble walking. Lead can cause high blood pressure, sleeping problems, anemia, headaches, and fatigue, etc. In daily life, we can exposure to heavy metal. Take lead as an example: 1. using kohl cosmetics; 2. applying hair dyes; 3. doing industrial work, and more. And it is difficult for the human body to withdraw those heavy metals, resulting, it slowly becomes poisonous over time.
Preventing heavy metal intoxication
Heavy metal test, can help determine if your essentral minerals and the overall level of heavy metals.
Depending on your result, we can customize a suitable detox program for you. At BMS, we apply two methods of heavy metal screening, (1) Toxic & Essential Elements; Hair (2) Toxic Metals; Urine.
We deliver the sample to a clinical laboratory, in the United States. Your sample will be tested in their facility. The test result will be available at an estimated time frame of 2 weeks. We will provide a detailed report of your result, once it is available.

Toxic & Essential Elements
Elements are the basic building blocks of all chemical compounds, and human exposure to them occurs both from natural and anthropogenic sources. Many elements are considered nutrients and are essential for the proper functioning of the body. These are generally divided between macrominerals such as calcium, magnesium, potassium, sodium, zinc, and trace minerals, including selenium, iodine, boron, and molybdenum.
Conversely, there are a number of elements that are toxic to the human body, interfere with its functioning and undermine health—such as mercury, lead, cadmium, aluminum, and arsenic. These toxic metals have no known physiological functions. They can be toxic to organ systems and may disrupt the balance of essential nutrients. Toxic metals and essential element status can be assessed in urine, blood, feces and hair.
BMS Clinic has always employed the best-available techniques as a specialist and pioneer in essential and toxic elemental testing. In fact, we were one of the first clinical reference laboratories in the world to employ ICP-MS and high-resolution ICP-MS for elemental analysis.
Reminders of preparation for the test:
- If you have any allergies, G6PD, or Kidney problems, please let your doctor know.
- If possible, avoid eating deep-sea fish and shell seafood before a week of collecting samples.
- Two days before collect samples, stop consuming supplements.
Heavy Metal Test Result
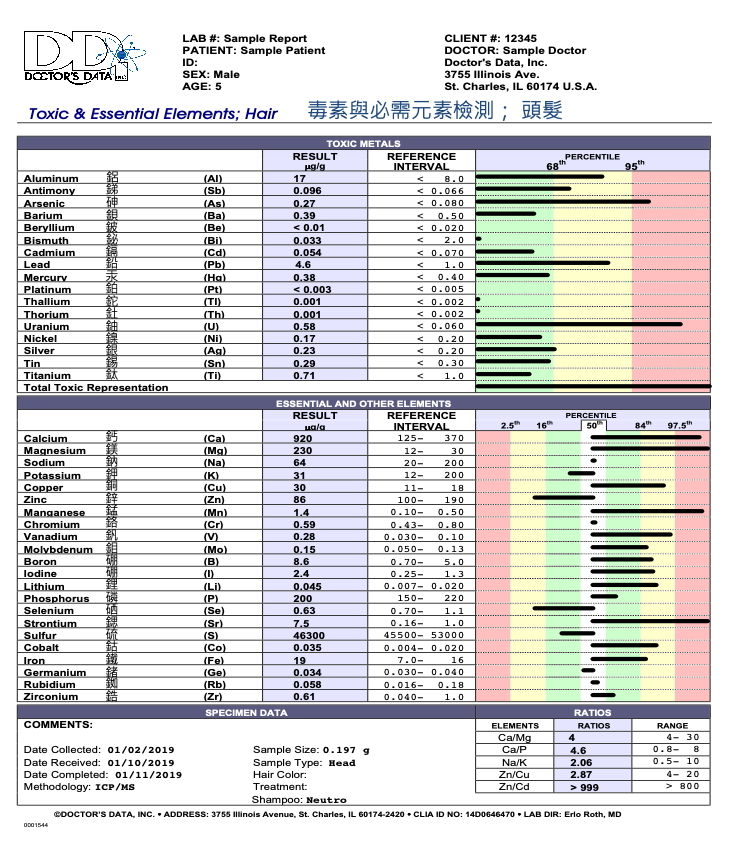
Hair - Toxic and Essential Elements
Hair Elements analysis provides information regarding recent and ongoing exposure to potentially toxic metals, especially methylmercury and arsenic, and the time-averaged status of specific nutrient elements. This non-invasive screening test requires only 0.25 grams of hair. Doctor’s Data offers a Hair Elements profile containing essential and toxic elements and a Hair Toxic Element Exposure profile containing an expanded lineup of toxic metals.
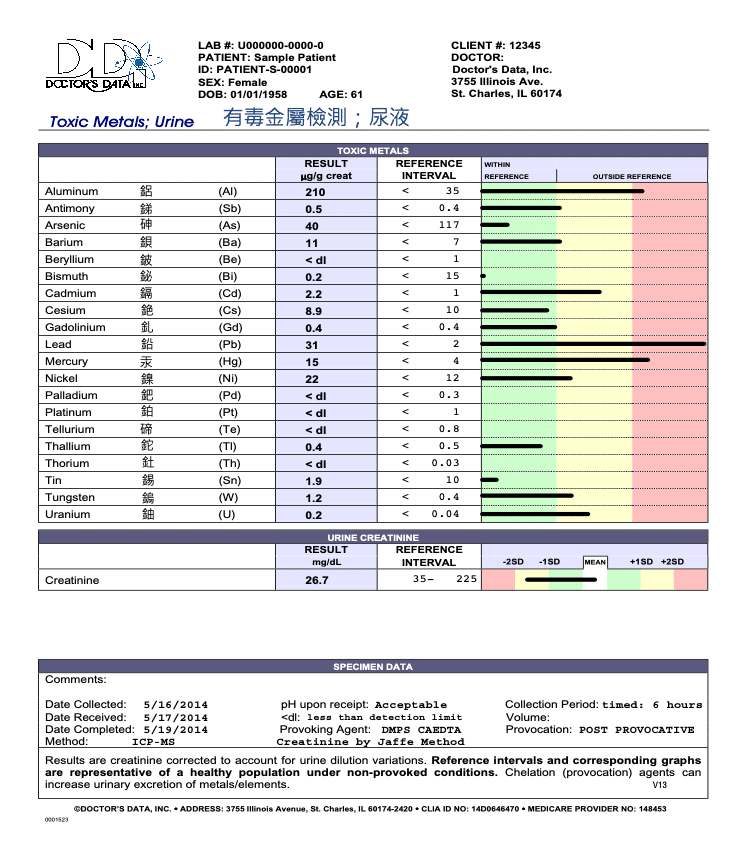
Urine - Toxic Metals
Urine Elements are traditionally used to evaluate exposure to potentially toxic elements and wasting of nutrient elements. Additionally, the comparison of urine element concentrations before and after administration of a chelator can be used to estimate the net retention of potentially toxic elements. Subsequent urine element analyses, also following the administration of a chelator, are useful for monitoring the efficacy of metal detoxification therapy.
Results and Follow-Up
The results of the heavy metal tests indicate the presence of specific heavy metals in your body.
If the levels are low, it is unlikely that you have heavy metal poisoning. However, if you continue to experience symptoms associated with heavy metal poisoning, you may discuss with your doctor to order additional tests to determine the underlying cause of your symptoms.
On the other hand, high levels of heavy metals could indicate heavy metal poisoning. In such cases, it is important for you to avoid further exposure to the specific metal for a certain period of time. Your healthcare provider will provide you with instructions on how to avoid exposure. If reducing your exposure does not lead to a decrease in your heavy metal levels, your provider may recommend chelation therapy. Chelation therapy involves the administration of medications through injections under the supervision of your healthcare provider, with the aim of removing excess metals from your body.
Through heavy metal testing, understanding personal health
Conversely, several elements are toxic to the human body, interfere with its functioning, and undermine health—such as mercury, lead, cadmium, aluminum, and arsenic. These toxic metals have no known physiological functions. They can be intoxicated to organ systems and may disrupt the balance of essential nutrients. Assessing Toxic metals and the status of the essential elements can be found in urine, blood, feces, and hair. Heavy metal testing can prevent heavy metals damage to organs. Reduce exposure to heavy metals in daily life. Also, be mindful of daily meals. Suggesting include Heavy metal testing in health checks yearly, which can make the health test more complete.
If heavy metals exceed the number of organ cells it can tolerate, it will damage the organ, causing anemia, diarrhea, nausea, and other symptoms.
FAQ
Heavy Metal Test
What is Heavy Metal Test?
In small amounts, these heavy metals are generally safe. However, excessive and long term exposure can lead to metal poisoning. If left untreated, overexposure to certain heavy metals can be life-threatening. If you exhibit symptoms of heavy metal poisoning, your healthcare provider may recommend a heavy metal test.
Cost of Heavy Metal Testing
If you are interested, feel free to contact us. We are here for you and optimize the best solution for your health.
Methods of Heavy Metal Testing?
(2) Toxic Metals; Urine.
How is it different from heavy metal testing offered elsewhere?
Our test can screen a variety range of toxic heavy metals (20 types). Most of the other service providers can only screen 5-6 types toxic heavy metals.
What are the signs of heavy metal poisoning?
The symptoms of heavy metal poisoning are often nonspecific and can be similar to other conditions. If you exhibit signs of metal poisoning, your healthcare provider may suggest undergoing a heavy metal test. These signs may include: <br>
Abdominal pain <br><br>
Chills <br>
Diarrhea <br>
Muscle weakness <br>
Nausea or vomiting <br>
Shortness of breath (dyspnea) <br>
Tingling in your hands or feet <br>
How long does it take the report result to be ready?
What is the difference between blood, urine, and hair or nail heavy metal test?
Blood sample: Measures mineral levels in the bloodstream, indicating recent exposure. Recommended for suspected sudden and significant heavy metal exposure.
Urine sample: Assesses toxic metal presence, especially in provocation testing. Evaluates the body’s response to metal release.
Hair (or nail) sample: Effective for assessing chronic mineral and toxic metal exposure. Provides insights into long-term mineral accumulation

